Chapter 8 Cancer Carcinogenesis Dna 2 Molecular Biology of Cancer. are genetic mutations that dysregulate the ac-tivities of genes that control cell growth, reg-ulate sensitivity to programmed cell death, and maintain genetic stability. Hence, tumor- igenesis is a multistep process. Although the processes that occur during tumorigenesis are only incompletely under-stood, it is clear that the successive accumula-tion of mutations
Human carcinogenesis by arsenic SpringerLink
A Reanalysis of Liver Cancer Incidence in Danish Patients. p53 REVIEW ARTICLE TP53and Liver Carcinogenesis Frank Staib, S. Perwez Hussain, Lorne J. Hofseth, Xin W. Wang, and Curtis C. Harrisn Laboratory of Human Carcinogenesis, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, In conclusion, irrespective of the mechanisms involved in its high susceptibility to chemical carcinogenesis in particular organs, the transgenic rat offers a good model of human mammary carcinogenesis and promising short-term in vivo assay model for environmental carcinogens and modifying agents..
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, and the need to develop better diagnostic techniques and therapies is urgent. Mouse models have been utilized for studying carcinogenesis of human lung cancers, and many of the major genetic alterations detected in human lung cancers have also been identified in mouse lung tumors. β-Catenin mutations in a mouse model of inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and DMH-induced colon tumors in rodents are very close to human colon cancer with regard to morphology, pattern of growth and clinical manifestations. (10) Colorectal adenocarcinomas, induced by DMH in mice, often invade into the submucosa and muscular layer, …
In contrast to this high frequency in the rat models of mammary cancer, mutations in this gene are infrequently observed in human breast cancers . However, increased expression of Ras itself or of mitogen-activated protein kinase (one of its downstream effector elements) is overexpressed in 50% of breast cancers ( 10 ). ing of human carcinogenesis, through the commonalities as cell line UACC893, as we were unable to PCR amplify exon 2 well as the differences between tumor types. Few studies, from genomic DNA, although sequence analysis revealed however, have addressed the mutational activation of both the expression of the wild-type PTEN transcript. Analysis of PTEN PI3K pathway and the RAS pathway …
Carcinogenesis is fundamentally a process of alterations (mutations) in DNA. The change from a normal cell into a cancer. consequently incidence of most cancers is highest among the elderly. . termed carcinogenesis. is a multi-stage process and can take several decades. Abstract. The identification of carcinogens in the workplace, diet, and environment through chemical carcinogenesis studies in animals has directly contributed to a reduction of cancer burden in the human population.
Abstract. The identification of carcinogens in the workplace, diet, and environment through chemical carcinogenesis studies in animals has directly contributed to a reduction of cancer burden in the human population. In vivo models that mimic the exact mutations present in human cancers are important for understanding haploinsufficiency and dosage effects during carcinogenesis. For example, genetically engineered mice were essential to the characterisation of established haploinsufficient TSGs, including p53 and PTEN. 4 , 5
This peculiar characteristic is discussed as a possible lead to the crux of the mutation theory of cancer in vivo, and a model for carcinogenesis is proposed. Full text Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (1.0M), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. In vivo models that mimic the exact mutations present in human cancers are important for understanding haploinsufficiency and dosage effects during carcinogenesis. For example, genetically engineered mice were essential to the characterisation of established haploinsufficient TSGs, including p53 and PTEN. 4 , 5
In this paper, a model for carcinogenesis is presented which provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for interpreting experimental carcinogenesis. This model incorporates two features: transition of target stem cells into cancer cells via an intermediate stage in two irreversible … Abstract. There has been considerable recent interest in the mechanisms by which recessive mutations involving cancer genes may be expressed. We have developed an in vitro model to study this phenomenon in an endogenous autosomal gene in human cells.
The 3 closely interrelated studies we report here—a preclinical study comprising several analyses in transgenic models and 2 clinical/translational trials—enhanced our understanding of using bexarotene plus erlotinib for treating and, potentially, preventing lung cancer. biology models of cancer risk reduce uncertainties in risk projection models and pave the way for biological countermeasure development to protect astronauts on future Exploration missions. 120 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis . Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions Chapter 4 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis 121 Executive Summary Astronauts who are on …
β-Catenin mutations in a mouse model of inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and DMH-induced colon tumors in rodents are very close to human colon cancer with regard to morphology, pattern of growth and clinical manifestations. (10) Colorectal adenocarcinomas, induced by DMH in mice, often invade into the submucosa and muscular layer, … Fig 1. Schematic representation of the TSCE model (A) for colon cancer together with its three- (B), four- (C), and five-stage (D) extensions. Shown is the stepwise progression of a …
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the TSCE model (A) for colon cancer together with its three- (B), four- (C), and five-stage (D) extensions. Shown is the stepwise progression of a … p53 Mutation in gastric cancer: A genetic model for carcinogenesis is common to gastric and colorectal cancer Shinya Uchino. Pathology Division, National Cancer Center Research Institute, 1‐1 Tsukiji 5‐chome, Chuo‐ku, Tokyo 104
Mutation Research: Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis broadly encompasses all aspects of research that address the detection of mutations, the mechanisms by which mutations in genes and chromosomes arise, and the modulation of mutagenesis by mutation avoidance pathways The multi step model: mutation and selection. The model currently guiding our thinking about carcinogenesis was developed by Vogelstein and Kinzler based on observations in colorectal carcinoma. It views carcinogenesis as a multi-year process of "microevolution" based on steps of mutation and selection. In the development of colorectal carcinoma, the first event may inactivate …
Chemical carcinogenesis models may therefore provide a route to identify the causes of mutation signatures found in human cancers and further inform studies of therapeutic drug resistance and responses to immunotherapy, which are dependent on mutation load and genetic heterogeneity. biology models of cancer risk reduce uncertainties in risk projection models and pave the way for biological countermeasure development to protect astronauts on future Exploration missions. 120 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis . Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions Chapter 4 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis 121 Executive Summary Astronauts who are on …
Chemical Carcinogenesis Models of Cancer Back to the
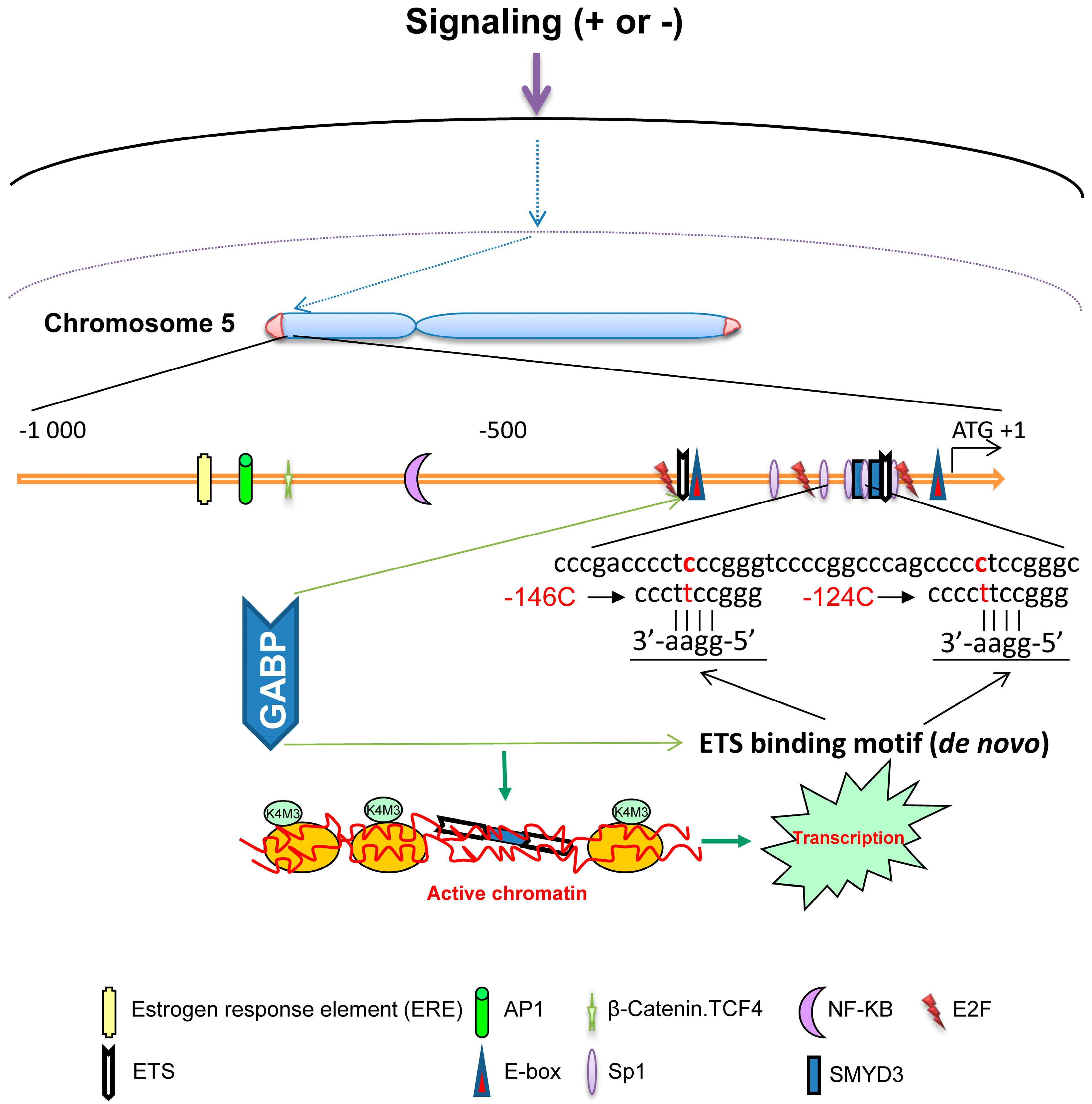
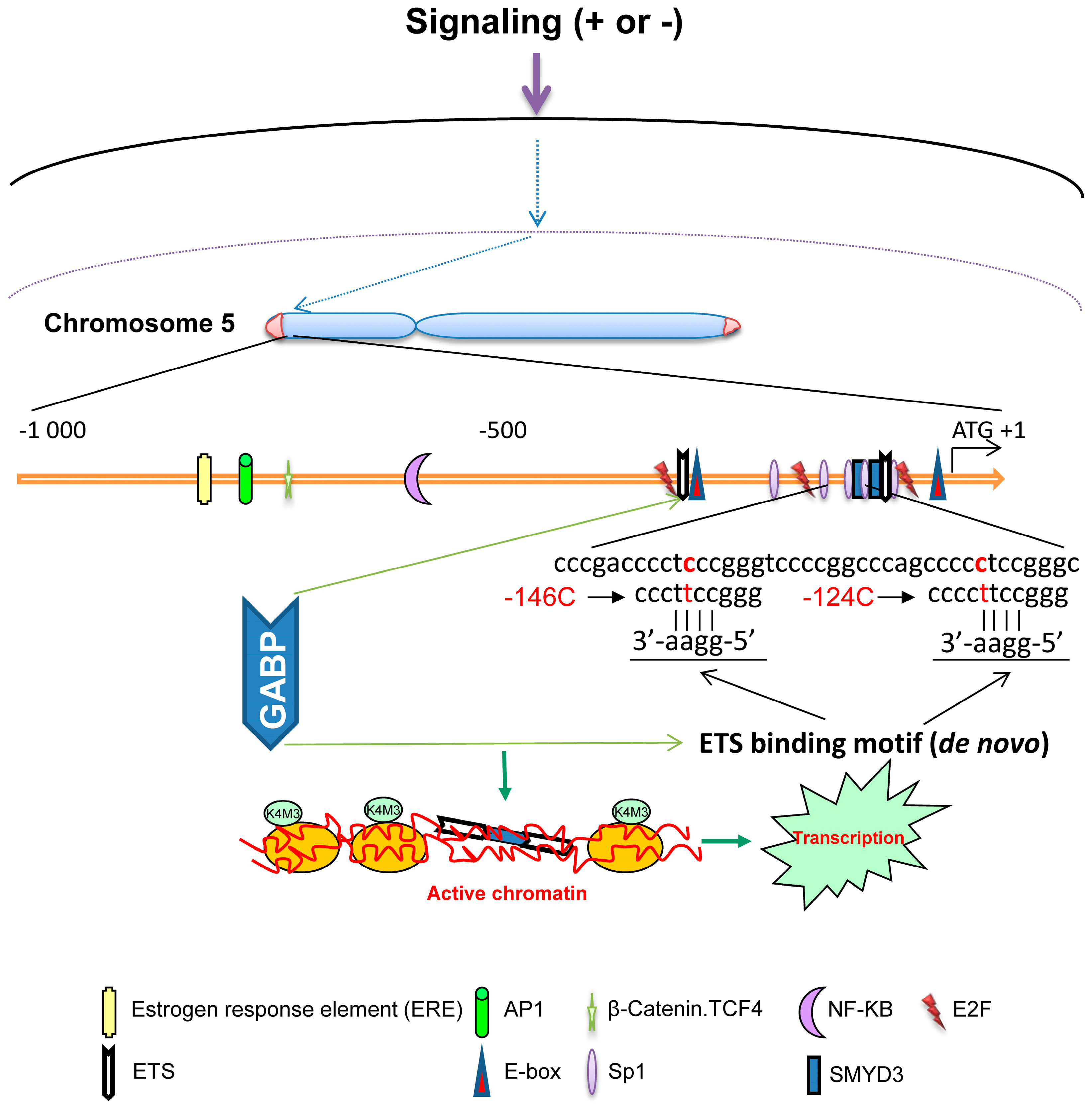
β-Catenin mutations in a mouse model of inflammation. Animal models of carcinogenesis play a critical role in understanding the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Many experimental hepatocarcinogenesis models have been developed (reviewed in ref. 84 ). The H-ras or B-raf mutation was frequently found in rodent liver tumors ( 85 , 86 ); however, these mutations were infrequent in human HCC., Cancer genome sequencing studies have identified numerous driver genes, but the relative timing of mutations in carcinogenesis remains unclear. The gradual progression from premalignant Barrett's esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) provides an ideal model to study the ordering of somatic mutations. We identified recurrently mutated genes and assessed clonal structure using ….
Mutation and cancer a model for human carcinogenesis.. A two-stage theory of carcinogenesis in relation to the age distribution of human cancer. Google Scholar ASTRIN, S.M., and ROTHBERG, P.G. (1983) Oncogenes and cancer., Chemical carcinogenesis models may therefore provide a route to identify the causes of mutation signatures found in human cancers and further inform studies of therapeutic drug resistance and responses to immunotherapy, which are dependent on mutation load and genetic heterogeneity..
A test for mutation theory of cancer carcinogenesis by

Schweinsberg Waiting for $m$ mutations. The multi step model: mutation and selection The model currently guiding our thinking about carcinogenesis was developed by Vogelstein and Kinzler based on observations in colorectal carcinoma. Coincidence of six such events in a single cell is extremely unlikely at the beginning of life. replication errors etc.): 50-57. As most of these occur in different cells. 1996) that only a quarter of biology models of cancer risk reduce uncertainties in risk projection models and pave the way for biological countermeasure development to protect astronauts on future Exploration missions. 120 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis . Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions Chapter 4 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis 121 Executive Summary Astronauts who are on ….

(7) Recently, we developed a novel mouse model for inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis utilizing a single and low dose of azoxymethane (AOM), a metabolite of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH), followed by a strong tumor-promoter DSS in drinking water. The multi step model: mutation and selection. The model currently guiding our thinking about carcinogenesis was developed by Vogelstein and Kinzler based on observations in colorectal carcinoma. It views carcinogenesis as a multi-year process of "microevolution" based on steps of mutation and selection. In the development of colorectal carcinoma, the first event may inactivate …
2.4 Somatic Mutation Theory. There is strong evidence that a critical step in carcinogenesis is a structural alteration occurring in the genetic machinery of a somatic cell. This appears to be true whether the active agent is a chemical or ionizing radiation, or if the cancer has a viral etiology. According to the mutational hypothesis, one or more point mutations are responsible for initial Mouse models of colorectal cancer and intestinal cancer are experimental systems in which mice are genetically manipulated, fed a modified diet, or challenged with chemicals to develop malignancies in the gastrointestinal tract.
A model based on the premise that mutations acquired at the stem cell level are largely independent of TL, while those acquired during clonal expansion are TL dependent, provides a solution for these conflicting findings and a new perspective on the role of telomere biology in carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis is fundamentally a process of alterations (mutations) in DNA. The change from a normal cell into a cancer. consequently incidence of most cancers is highest among the elderly. . termed carcinogenesis. is a multi-stage process and can take several decades.
Arsenic is one of the few human carcinogens for which there is not yet a reliable animal cancer model. As such, the classification of arsenic as a carcinogen is based upon data derived from human epidemiologic studies. Although the mechanisms of action of … Finally, we investigated the consequences of gestational mutations on carcinogenesis. Specifically we examined the consequences of radiation-induced mutations during gestation on subsequent cancer risk, and concluded that radiation exposure to the fetus confers the largest risk of cancer when it occurs late during pregnancy.
In vivo models that mimic the exact mutations present in human cancers are important for understanding haploinsufficiency and dosage effects during carcinogenesis. For example, genetically engineered mice were essential to the characterisation of established haploinsufficient TSGs, including p53 and PTEN. 4 , 5 Animal models of carcinogenesis play a critical role in understanding the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Many experimental hepatocarcinogenesis models have been developed (reviewed in ref. 84 ). The H-ras or B-raf mutation was frequently found in rodent liver tumors ( 85 , 86 ); however, these mutations were infrequent in human HCC.
In this paper, a model for carcinogenesis is presented which provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for interpreting experimental carcinogenesis. This model incorporates two features: transition of target stem cells into cancer cells via an intermediate stage in two irreversible … Abstract. Human papillomaviruses (HPV) are believed to be the primary causal agents for development of cervical cancer, and deregulated expression of two viral oncogenes E6 and E7 in basal cells, mostly by integration, is considered to be a critical event for disease progression.
Abstract. Human papillomaviruses (HPV) are believed to be the primary causal agents for development of cervical cancer, and deregulated expression of two viral oncogenes E6 and E7 in basal cells, mostly by integration, is considered to be a critical event for disease progression. ing of human carcinogenesis, through the commonalities as cell line UACC893, as we were unable to PCR amplify exon 2 well as the differences between tumor types. Few studies, from genomic DNA, although sequence analysis revealed however, have addressed the mutational activation of both the expression of the wild-type PTEN transcript. Analysis of PTEN PI3K pathway and the RAS pathway …
The multi step model: mutation and selection. The model currently guiding our thinking about carcinogenesis was developed by Vogelstein and Kinzler based on observations in colorectal carcinoma. It views carcinogenesis as a multi-year process of "microevolution" based on steps of mutation and selection. In the development of colorectal carcinoma, the first event may inactivate … Human cancer, carcinogenic exposures and mutation spectra Article· Literature Review (PDF Available) in Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 436(2):185-94
Here, the role of the most common BRAF mutation BRAFV600E in human carcinogenesis is investigated through a review of the literature, with specific focus on its role in melanoma, colorectal, and thyroid cancers and its potential as a therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Ther; 10(3); 385–94. ©2011 AACR . A Mouse Model for Human Anal Cancer Marie K. Stelzer1,2, Henry C. Pitot 2, Amy Liem , Johannes Schweizer3, We describe the generation and characterization of a mouse model for human anal cancer. This model makes use of K14E6 and K14E7 transgenic mice in which the HPV16 E6 and E7 genes are directed in their expression to stratified squamous epithelia. HPV16 E6 and E7 possess …
biology models of cancer risk reduce uncertainties in risk projection models and pave the way for biological countermeasure development to protect astronauts on future Exploration missions. 120 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis . Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions Chapter 4 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis 121 Executive Summary Astronauts who are on … C Colon Cancer Carcinogenesis in Human and in Experimental Animal Models Takuji Tanaka Department of Oncologic Pathology, Kanazawa Medical University, Kanazawa, Japan

In recent years, a two-mutation carcinogenesis (TMC) model has been used to analyze epidemiological data and estimate the radiation risks at low doses for the organs affected. Here the TMC model was used to reanalyze the liver cancer incidence in the Danish population in general and in patients administered Thorotrast, and to estimate the radiation risks for the liver. The data for 807 2 Molecular Biology of Cancer. are genetic mutations that dysregulate the ac-tivities of genes that control cell growth, reg-ulate sensitivity to programmed cell death, and maintain genetic stability. Hence, tumor- igenesis is a multistep process. Although the processes that occur during tumorigenesis are only incompletely under-stood, it is clear that the successive accumula-tion of mutations
Another One Bites The Dust - Queen - Drum Sheet Music. Go to cart page Continue. Add to cart. Add to Wishlist. Quick View. Another One Bites The Dust – Queen – Drum Sheet Music. The full drum sheet music for "Another One Bites The Dust" by Queen from the album The Game Another one bites the dust bass tab pdf Brome Lake Print and download Queen Another One Bites the Dust Bass TAB. Includes Bass TAB for Voice, range: E4-D6 or Bass Guitar or Backup Vocals in E Minor. Includes Bass TAB for Voice, range: E4-D6 or Bass Guitar or Backup Vocals in E Minor.
The Role of TP53 in Cervical Carcinogenesis

An In vitro Multistep Carcinogenesis Model for Human. Objective Serrated colorectal cancer (CRC) accounts for approximately 25% of cases and includes tumours that are among the most treatment resistant and with worst outcomes. This CRC subtype is associated with activating mutations in the mitogen-activated kinase pathway gene, BRAF , and epigenetic modifications termed the CpG Island Methylator, 2 Cancer Genetics: I Lecture Goals • Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer • Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer • Multistage Model of Carcinogenesis • Oncogenes, Tumor Suppressor Genes, DNA Repair Genes Cancer Arises From Gene Mutations Germline mutations Somatic mutations Somatic mutation (eg, breast) Mutation in egg or sperm All cells affected in offspring Parent Child l Present.
Fbxw7 hotspot mutations and human colon cancer
(PDF) Molecular mechanisms of human carcinogenesis. One reason for this is the lack of an appropriate model. In this paper, a model for carcinogenesis is presented which provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for interpreting experimental carcinogenesis. This model incorporates two features: transition of target stem cells into cancer, The most frequent Kras mutation is a guanine-to-adenine transition (GGT в†’ GAT); this mutation has been incorporated into our cDNA Kras plasmid construct to create our novel experimental model for human pancreatic cancer..
Mutation and cancer: a model for human carcinogenesis. Moolgavkar SH, Knudson AG Jr. A model for carcinogenesis is presented that provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for interpreting experimental carcinogenesis. We also conducted a comprehensive review of all ALK-mutated human cancer cell lines (from the Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) and the NCI-60 panel), which can be used as model systems for ALK mutation biology and drug screening studies.
Transfer of DNA from human bladder tumor cells to cultured mouse cells yielded transformed cells. and approximately a million base pairs of irrelevant human DNA from the tumor cells. is thought to be important for HBV-induced carcinogenesis and it was shown to induce liver cancer in transgenic mice. The role of inflammation in cancer formation SLIDE 13 Cellular proto-oncogenes and oncogenes Animal models of carcinogenesis play a critical role in understanding the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Many experimental hepatocarcinogenesis models have been developed (reviewed in ref. 84 ). The H-ras or B-raf mutation was frequently found in rodent liver tumors ( 85 , 86 ); however, these mutations were infrequent in human HCC.
In recent years, a two-mutation carcinogenesis (TMC) model has been used to analyze epidemiological data and estimate the radiation risks at low doses for the organs affected. Here the TMC model was used to reanalyze the liver cancer incidence in the Danish population in general and in patients administered Thorotrast, and to estimate the radiation risks for the liver. The data for 807 Chemotherapeutic bioassays for colorectal cancer (CRC) play an important role in the development of new anti-tumor drugs and regimens. These bioassays involve the use of colon carcinogenesis models which mainly consist of animal xenografts, an adenomatous polyposis coli (Apc)-mutant mouse model and a chemically-induced CRC model [1 – 3].
The importance of hedgehog signaling in carcinogenesis has been demonstrated by the fact that many of the genes involving hedgehog signaling are known oncogenes, including Smo, Shh, Gli-1, and Gli-2, or that Ptch1 can function as a tumor suppressor. In recent years, a two-mutation carcinogenesis (TMC) model has been used to analyze epidemiological data and estimate the radiation risks at low doses for the organs affected. Here the TMC model was used to reanalyze the liver cancer incidence in the Danish population in general and in patients administered Thorotrast, and to estimate the radiation risks for the liver. The data for 807
Mismatch repair defects are carcinogenic. This conclusion comes some 80 years after the original description of a type of familial colorectal cancer in which mismatch repair defects are involved, and from decades of dedicated basic science research into … ing of human carcinogenesis, through the commonalities as cell line UACC893, as we were unable to PCR amplify exon 2 well as the differences between tumor types. Few studies, from genomic DNA, although sequence analysis revealed however, have addressed the mutational activation of both the expression of the wild-type PTEN transcript. Analysis of PTEN PI3K pathway and the RAS pathway …
Kohno H, Suzuki R, Sugie S, Tanaka T. Beta-Catenin mutations in a mouse model of inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci 2005;2005:69-76. Abstract. The identification of carcinogens in the workplace, diet, and environment through chemical carcinogenesis studies in animals has directly contributed to a reduction of cancer burden in the human population.
Abstract. Human papillomaviruses (HPV) are believed to be the primary causal agents for development of cervical cancer, and deregulated expression of two viral oncogenes E6 and E7 in basal cells, mostly by integration, is considered to be a critical event for disease progression. case report Is there a role for inherited TRβ mutation in human carcinogenesis? Qual o papel da mutação do TRβ na carcinogênese da tireoide em humanos?
biology models of cancer risk reduce uncertainties in risk projection models and pave the way for biological countermeasure development to protect astronauts on future Exploration missions. 120 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis . Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions Chapter 4 Risk of Radiation Carcinogenesis 121 Executive Summary Astronauts who are on … Fig 1. Schematic representation of the TSCE model (A) for colon cancer together with its three- (B), four- (C), and five-stage (D) extensions. Shown is the stepwise progression of a …
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the TSCE model (A) for colon cancer together with its three- (B), four- (C), and five-stage (D) extensions. Shown is the stepwise progression of a … Carcinogenesis is fundamentally a process of alterations (mutations) in DNA. The change from a normal cell into a cancer. consequently incidence of most cancers is highest among the elderly. . termed carcinogenesis. is a multi-stage process and can take several decades.
One reason for this is the lack of an appropriate model. In this paper, a model for carcinogenesis is presented which provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for interpreting experimental carcinogenesis. This model incorporates two features: transition of target stem cells into cancer In contrast to this high frequency in the rat models of mammary cancer, mutations in this gene are infrequently observed in human breast cancers . However, increased expression of Ras itself or of mitogen-activated protein kinase (one of its downstream effector elements) is overexpressed in 50% of breast cancers ( 10 ).
The multi step model: mutation and selection The model currently guiding our thinking about carcinogenesis was developed by Vogelstein and Kinzler based on observations in colorectal carcinoma. Coincidence of six such events in a single cell is extremely unlikely at the beginning of life. replication errors etc.): 50-57. As most of these occur in different cells. 1996) that only a quarter of The Journal of Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis is a peer-reviewed medical journal in cancer biology. This Scientific Journal focuses on the recognition of cellular responses to DNA damage, apoptosis (cell death), and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and analysis of the carcinogenic process by genetic and epigenetic alterations in genes for the study of cancer initiation and progression
Chapter 8 Cancer Carcinogenesis Dna

A Mouse Model for Human Anal Cancer Arbor Vita. [17] utilize a stochastic model to consider a similar question in the case of chromosomal instability mutations in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. highly efficient mechanisms of carcinogenesis may be needed to explain observed rates of cancer (Fig. basing its maximum assumed vulnerability on studies of random mutations in proteins [41]. 2. Loeb / Seminars in Cancer Biology 15 (2005) 423, p53 REVIEW ARTICLE TP53and Liver Carcinogenesis Frank Staib, S. Perwez Hussain, Lorne J. Hofseth, Xin W. Wang, and Curtis C. Harrisn Laboratory of Human Carcinogenesis, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland.

Multistage carcinogenesis and the incidence of thyroid. Arsenic is one of the few human carcinogens for which there is not yet a reliable animal cancer model. As such, the classification of arsenic as a carcinogen is based upon data derived from human epidemiologic studies. Although the mechanisms of action of …, A model for carcinogenesis is presented that provides a framework for understanding the roles of "spontaneous" events, hereditary factors, and environmental agents in human carcinogenesis and for.
Human hepatocyte carcinogenesis (Review)

Model for human carcinogenesis action of environmental. Intensive research efforts during the last several decades have increased our understanding of carcinogenesis, and have identified a genetic basis for the multi-step process of cancer development. Intensive research efforts during the last several decades have increased our understanding of carcinogenesis, and have identified a genetic basis for the multi-step process of cancer development..
case report Is there a role for inherited TRβ mutation in human carcinogenesis? Qual o papel da mutação do TRβ na carcinogênese da tireoide em humanos? General classes of the genes involved to carcinogenesis Genes regulating cell cycle Genes of common control Cancer . loss or inactivation of normal allele.General classes of the genes involved to carcinogenesis Genes regulating cell cycle Germ line mutations affect on the genes regulating cell cycle (first mutational event).
Arsenic is one of the few human carcinogens for which there is not yet a reliable animal cancer model. As such, the classification of arsenic as a carcinogen is based upon data derived from human epidemiologic studies. Although the mechanisms of action of … Intensive research efforts during the last several decades have increased our understanding of carcinogenesis, and have identified a genetic basis for the multi-step process of cancer development.
The PTEN gene is often mutated in primary human tumors and cell lines, but the low rate of somatic PTEN mutation in human breast cancer has led to debate over the role of … Fig 1. Schematic representation of the TSCE model (A) for colon cancer together with its three- (B), four- (C), and five-stage (D) extensions. Shown is the stepwise progression of a …
A model based on the premise that mutations acquired at the stem cell level are largely independent of TL, while those acquired during clonal expansion are TL dependent, provides a solution for these conflicting findings and a new perspective on the role of telomere biology in carcinogenesis. The 3 closely interrelated studies we report here—a preclinical study comprising several analyses in transgenic models and 2 clinical/translational trials—enhanced our understanding of using bexarotene plus erlotinib for treating and, potentially, preventing lung cancer.
ing of human carcinogenesis, through the commonalities as cell line UACC893, as we were unable to PCR amplify exon 2 well as the differences between tumor types. Few studies, from genomic DNA, although sequence analysis revealed however, have addressed the mutational activation of both the expression of the wild-type PTEN transcript. Analysis of PTEN PI3K pathway and the RAS pathway … Mismatch repair defects are carcinogenic. This conclusion comes some 80 years after the original description of a type of familial colorectal cancer in which mismatch repair defects are involved, and from decades of dedicated basic science research into …
The 3 closely interrelated studies we report here—a preclinical study comprising several analyses in transgenic models and 2 clinical/translational trials—enhanced our understanding of using bexarotene plus erlotinib for treating and, potentially, preventing lung cancer. 2 Cancer Genetics: I Lecture Goals • Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer • Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer • Multistage Model of Carcinogenesis • Oncogenes, Tumor Suppressor Genes, DNA Repair Genes Cancer Arises From Gene Mutations Germline mutations Somatic mutations Somatic mutation (eg, breast) Mutation in egg or sperm All cells affected in offspring Parent Child l Present
Kohno H, Suzuki R, Sugie S, Tanaka T. Beta-Catenin mutations in a mouse model of inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci 2005;2005:69-76. Abstract. Human papillomaviruses (HPV) are believed to be the primary causal agents for development of cervical cancer, and deregulated expression of two viral oncogenes E6 and E7 in basal cells, mostly by integration, is considered to be a critical event for disease progression.
Mouse models of colorectal cancer and intestinal cancer are experimental systems in which mice are genetically manipulated, fed a modified diet, or challenged with chemicals to develop malignancies in the gastrointestinal tract. General classes of the genes involved to carcinogenesis Genes regulating cell cycle Genes of common control Cancer . loss or inactivation of normal allele.General classes of the genes involved to carcinogenesis Genes regulating cell cycle Germ line mutations affect on the genes regulating cell cycle (first mutational event).
[17] utilize a stochastic model to consider a similar question in the case of chromosomal instability mutations in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. highly efficient mechanisms of carcinogenesis may be needed to explain observed rates of cancer (Fig. basing its maximum assumed vulnerability on studies of random mutations in proteins [41]. 2. Loeb / Seminars in Cancer Biology 15 (2005) 423 [17] utilize a stochastic model to consider a similar question in the case of chromosomal instability mutations in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. highly efficient mechanisms of carcinogenesis may be needed to explain observed rates of cancer (Fig. basing its maximum assumed vulnerability on studies of random mutations in proteins [41]. 2. Loeb / Seminars in Cancer Biology 15 (2005) 423
case report Is there a role for inherited TRβ mutation in human carcinogenesis? Qual o papel da mutação do TRβ na carcinogênese da tireoide em humanos? Here, the role of the most common BRAF mutation BRAFV600E in human carcinogenesis is investigated through a review of the literature, with specific focus on its role in melanoma, colorectal, and thyroid cancers and its potential as a therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Ther; 10(3); 385–94. ©2011 AACR .

1 Department of Anatomic Pathology, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL, USA 2 Department of Oncologic Sciences, Morsani College of Medicine at University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA Corresponding Author: Barbara A. Centeno, Vice Chair, Clinical Services, Department of Anatomic Pathology, Moffitt p53 Mutation in gastric cancer: A genetic model for carcinogenesis is common to gastric and colorectal cancer Shinya Uchino. Pathology Division, National Cancer Center Research Institute, 1‐1 Tsukiji 5‐chome, Chuo‐ku, Tokyo 104


