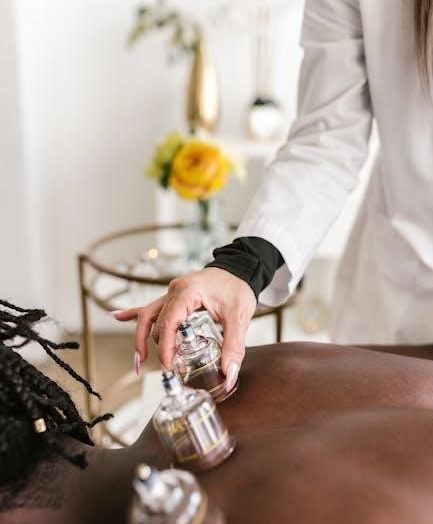
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) is a holistic, hands-on approach addressing pain, injuries, and body function by treating all systems—circulatory, nervous, lymphatic, and endocrine—to promote self-healing and optimal health.
1.1 Definition and Overview
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) is a holistic, hands-on therapeutic approach that combines advanced manual techniques to address pain, dysfunction, and disability. It focuses on treating the root cause of issues by assessing and restoring balance across all body systems, including circulatory, nervous, lymphatic, and endocrine. IMT emphasizes the body’s innate ability to self-correct and heal, promoting optimal health and well-being. This method is known for its comprehensive approach, addressing physical, emotional, and systemic factors to achieve lasting results.
1.2 Historical Background
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) has evolved from a combination of manual therapy traditions, drawing on osteopathic principles, physical therapy techniques, and holistic healing practices. Its development spans decades, integrating diverse approaches to create a comprehensive system. IMT emerged as a distinct method in the late 20th century, emphasizing the body’s self-healing potential. It has since grown into a recognized modality, blending advanced diagnostic and treatment strategies. Practitioners continue to refine IMT, making it a dynamic and evolving field in holistic healthcare.
1.3 Key Principles and Philosophy
Integrative Manual Therapy is rooted in a holistic philosophy, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the body’s systems. It integrates manual techniques with other therapeutic modalities to address the whole person—physical, emotional, and mental. A core principle is the body’s innate ability to self-correct and heal when guided appropriately. The approach values collaboration between therapist and patient, fostering a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs. This methodology aims to restore balance, enhance function, and promote overall well-being, empowering individuals to actively participate in their health journey.
Core Concepts of Integrative Manual Therapy
IMT combines manual techniques, holistic health approaches, and integrative modalities to address physical, emotional, and mental well-being, emphasizing the body’s self-healing potential and systemic interconnectedness.
2.1 The Role of Manual Techniques
Manual techniques in IMT are central to diagnosing and treating physical dysfunction. They involve gentle, hands-on methods like soft tissue manipulation and joint mobilization to restore movement, reduce pain, and enhance overall body function. These techniques aim to address imbalances in the body’s systems, promoting self-correction and healing. By targeting specific areas, manual therapy improves circulation, reduces tension, and supports the body’s natural recovery processes. This approach is tailored to individual needs, fostering a collaborative environment between therapist and patient. The goal is to empower the body to heal itself effectively, ensuring long-term wellness and optimal function.
2.2 Holistic Approach to Health
Integrative Manual Therapy adopts a holistic approach, treating the whole person—body, mind, and spirit. It views health as a balance of interconnected systems, addressing physical, emotional, and mental well-being. By considering the entire individual, IMT aims to restore harmony and optimal function. This approach emphasizes the body’s innate ability to heal itself when proper conditions are created. It encourages patient empowerment and self-awareness, fostering a collaborative relationship between therapist and client. The holistic nature of IMT ensures comprehensive care, addressing root causes rather than just symptoms.
2.3 Integration of Multiple Therapeutic Modalities
Integrative Manual Therapy seamlessly combines various therapeutic techniques, creating a tailored approach for each client. It merges soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, myofascial release, and lymphatic techniques to address diverse health issues. By integrating these modalities, IMT treats the body as a unified system, enhancing overall function and well-being. This multi-faceted method allows therapists to adapt treatments to individual needs, ensuring a comprehensive and effective healing process that fosters balance and optimal health outcomes.

Techniques and Methods Used in IMT
Integrative Manual Therapy employs soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, myofascial release, and lymphatic techniques to restore body function and promote healing through a holistic approach.
3.1 Soft Tissue Manipulation
Soft tissue manipulation in IMT involves gentle, targeted techniques to address pain, stiffness, and restricted motion in muscles, tendons, and ligaments. By applying precise pressure and movements, therapists restore balance to soft tissues, improving circulation and reducing inflammation. This approach enhances flexibility, alleviates tension, and promotes overall musculoskeletal health. Soft tissue work is integral to IMT, as it supports the body’s natural healing processes and fosters a state of relaxation and well-being; It is often combined with other methods to address the root causes of discomfort and dysfunction.
3.2 Joint Mobilization and Alignment
Joint mobilization and alignment in IMT focus on restoring proper joint mechanics and reducing stiffness. Gentle, precise movements target joint dysfunctions, improving range of motion and relieving pain. This technique addresses structural imbalances, enhances mobility, and reduces muscle spasms. By aligning joints correctly, it promotes optimal function and reduces strain on surrounding tissues. Joint mobilization is a key component of IMT, often combined with soft tissue work to achieve comprehensive relief and improve overall musculoskeletal well-being. It is particularly effective for addressing chronic pain and mobility issues.
3.3 Myofascial Release
Myofascial release in IMT targets the fascia, a connective tissue surrounding muscles, nerves, and organs. Gentle, sustained pressure is applied to release fascial restrictions, improving circulation and reducing tension. This technique alleviates pain, enhances flexibility, and restores normal movement. By addressing fascial adhesions, it promotes relaxation and reduces muscle spasms. Myofascial release is integral to IMT, often used alongside other modalities to address chronic pain, scar tissue, and limited mobility. Its non-invasive approach makes it suitable for various conditions, fostering overall musculoskeletal balance and well-being.
3.4 Lymphatic and Circulatory Techniques
Lymphatic and circulatory techniques in IMT focus on enhancing blood and lymph flow to promote healing and detoxification. Gentle manual methods improve circulation, reducing swelling and supporting immune function. These techniques address restrictions in the lymphatic system, aiding in toxin removal and tissue repair. By boosting blood flow, they deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells, fostering recovery and overall well-being. This approach is integral to IMT, offering a non-invasive way to support bodily functions and maintain health.

Benefits of Integrative Manual Therapy
Integrative Manual Therapy promotes overall health, enhances self-healing, and improves well-being by addressing physical and emotional needs holistically.
4.1 Pain Relief and Management
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) offers effective pain relief by addressing the root cause of discomfort. By targeting soft tissue, joints, and fascia, IMT reduces inflammation and restores alignment. This approach enhances circulation, relaxes muscles, and promotes healing. Many patients experience significant reduction in chronic pain, improved mobility, and emotional relief. IMT’s holistic methods create a sustainable environment for long-term pain management, empowering individuals to regain control over their well-being.
4.2 Improved Mobility and Flexibility
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) enhances mobility and flexibility by releasing tension in soft tissues and improving joint function. Techniques like joint mobilization and myofascial release break down adhesions, restoring natural movement. This approach promotes fluidity in the body, allowing for better range of motion and reduced stiffness. Improved circulation and muscle relaxation further support flexibility, enabling individuals to perform daily activities and physical endeavors with greater ease and efficiency. IMT’s focus on whole-body alignment ensures sustainable gains in mobility and flexibility.
4.3 Enhanced Emotional and Mental Well-being
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) fosters emotional and mental well-being by addressing the mind-body connection. By releasing physical tension, IMT reduces stress and anxiety, promoting relaxation and calm. The therapy enhances mood and emotional resilience, helping individuals manage psychological challenges. Its holistic approach supports self-awareness and emotional balance, leading to improved mental health and overall well-being.
4.4 Promotion of Overall Health and Wellness
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) promotes overall health by addressing the body’s interconnected systems, enhancing circulation, nervous system function, and cellular health. It supports the body’s natural healing processes, improving physical, emotional, and mental well-being. By restoring balance and function, IMT empowers individuals to maintain optimal health, reducing the risk of chronic conditions and fostering vitality. This holistic approach creates a foundation for long-term wellness, enabling individuals to thrive in all aspects of life.

Applications of Integrative Manual Therapy
IMT is applied in chronic pain management, sports injuries, stress reduction, and addressing neurological or musculoskeletal disorders, promoting holistic healing and overall well-being through targeted techniques.
5.1 Chronic Pain Management
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) offers a comprehensive approach to chronic pain management by addressing the root causes of discomfort. By targeting soft tissue, joints, and systemic imbalances, IMT promotes self-healing and restores function. Techniques such as myofascial release and lymphatic drainage help alleviate persistent pain, reducing reliance on medications. This holistic method empowers patients to regain control over their bodies, enhancing mobility and overall well-being. IMT’s focus on the interconnectedness of body systems makes it an effective solution for chronic pain, fostering long-term relief and improved quality of life.
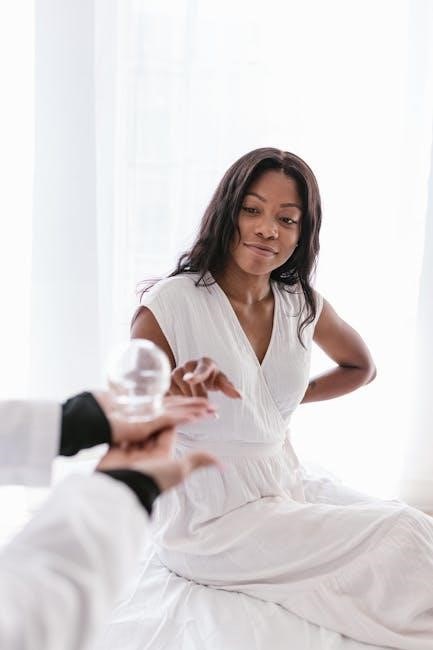

5.2 Sports Injuries and Rehabilitation
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) is highly effective in addressing sports injuries and rehabilitation by targeting the root causes of dysfunction. Its holistic approach combines soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, and myofascial release to restore mobility and strength. IMT accelerates recovery, reduces inflammation, and enhances athletic performance. By addressing musculoskeletal imbalances, it prevents future injuries and supports overall physical resilience. This method is particularly beneficial for athletes, promoting faster return to activity while improving flexibility and endurance, making it a cornerstone in modern sports rehabilitation practices.
5.3 Stress Reduction and Relaxation
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) plays a significant role in stress reduction and relaxation by addressing the body’s physiological and emotional responses. Techniques such as myofascial release and soft tissue manipulation help calm the autonomic nervous system, promoting a state of deep relaxation. IMT also enhances circulation and reduces muscle tension, which are often heightened during stress. By restoring balance to the body’s systems, IMT fosters emotional well-being, reducing anxiety and improving sleep quality. This holistic approach creates a therapeutic environment where individuals can achieve mental and physical calm, essential for long-term stress management and overall health.
5.4 Addressing Neurological and Musculoskeletal Disorders
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) effectively addresses neurological and musculoskeletal disorders by targeting the root causes of dysfunction. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation restore alignment and mobility, reducing inflammation and pain. IMT also enhances nervous system regulation, improving communication between the brain and body. This holistic approach helps manage conditions like chronic pain, sciatica, and even neurological impairments, fostering recovery and functional improvement. By addressing both the structural and systemic aspects, IMT provides comprehensive care for complex musculoskeletal and neurological challenges.
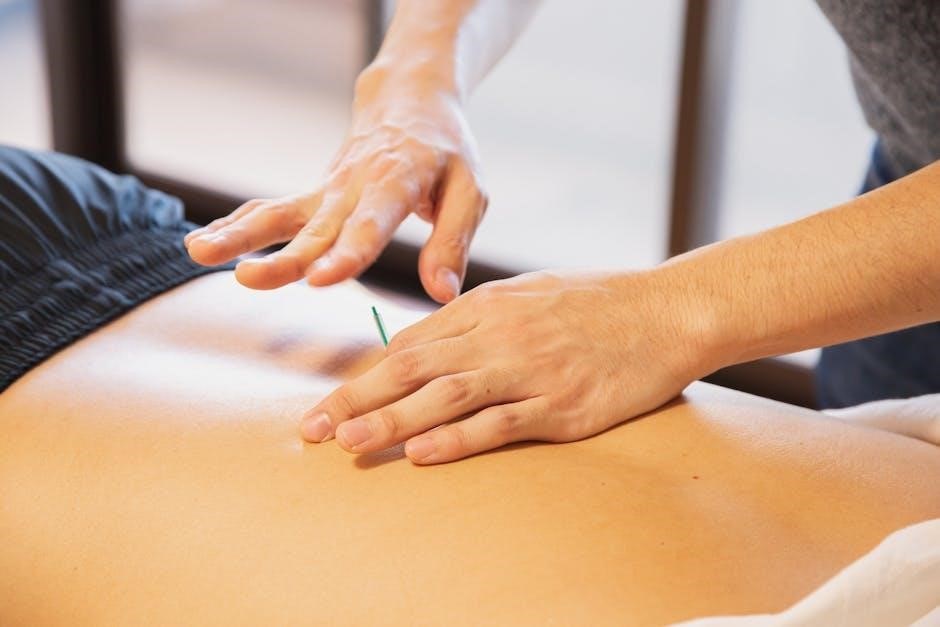

The Role of the Therapist in IMT
The IMT therapist collaborates with patients, creating personalized plans to address their needs, while using specialized techniques to promote healing and overall well-being through manual interventions.
6.1 Therapist-Patient Collaboration
Therapist-patient collaboration in IMT is essential for effective treatment. The therapist works closely with the patient to understand their specific needs and goals, ensuring a tailored approach. This partnership fosters trust and active participation, enabling the patient to take an integral role in their healing process. Open communication allows the therapist to adjust techniques and strategies based on real-time feedback, enhancing the therapy’s effectiveness and promoting a more personalized and holistic treatment experience.
6.2 Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are a cornerstone of IMT, ensuring each patient receives care tailored to their unique needs. By assessing the individual’s health, lifestyle, and specific challenges, therapists create customized strategies to address pain, restore function, and enhance well-being. These plans integrate various techniques, focusing on the root causes of dysfunction rather than symptoms alone. Regular adjustments are made based on progress, ensuring the therapy remains effective and aligned with the patient’s evolving goals, fostering a pathway to optimal health and resilience.
6.3 Continuous Education and Skill Development
Continuous education and skill development are vital for IMT therapists to stay updated with the latest techniques and research. Regular workshops, advanced training, and peer collaboration ensure therapists maintain high standards of practice. By committing to lifelong learning, they refine their diagnostic and treatment skills, enabling them to address complex cases effectively. This dedication to professional growth ensures IMT remains a dynamic and evolving field, offering innovative solutions for patient care and optimal outcomes.

Scientific Evidence and Research
Research highlights IMT’s effectiveness in pain relief and mobility improvement, supported by studies on neurophysiological responses and self-correction, enhancing its acceptance in modern therapeutic practices.
7.1 Studies on the Efficacy of IMT
Studies demonstrate IMT’s effectiveness in addressing pain and improving mobility by targeting the body’s circulatory, nervous, and lymphatic systems. Research highlights its ability to promote self-correction and healing, with positive outcomes in chronic pain management and injury recovery. IMT’s holistic approach is supported by evidence showing enhanced neurophysiological responses, making it a recognized method in modern therapeutic practices. Its integration of multiple modalities ensures comprehensive care, addressing the root causes of dysfunction and fostering overall well-being.
7.2 Neurophysiological Responses to Manual Therapy
Manual therapy in IMT triggers neurophysiological responses, enhancing the body’s ability to heal. Techniques Activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and promoting relaxation. This activation fosters a conducive environment for self-correction and tissue repair. Studies show improved blood flow and reduced inflammation, alongside the release of endorphins, which alleviate pain. These responses highlight the interconnectedness of manual interventions with the nervous system, demonstrating how IMT can restore balance and function at a cellular level, ultimately enhancing overall well-being and physiological harmony.
7.3 The Role of Self-Correction and Body Awareness
Integrative Manual Therapy emphasizes the body’s innate ability to self-correct, fostering healing through gentle, non-invasive techniques. By enhancing body awareness, patients gain insight into their physiological and emotional states, empowering them to actively participate in recovery. This mindfulness allows individuals to better respond to their body’s needs, facilitating deeper healing and long-term well-being, aligning with IMT’s holistic approach to health and self-recovery.
Training and Certification in IMT
IMT certification requires extensive education, hands-on training, and mastery of manual techniques. Therapists must complete rigorous programs, ensuring proficiency in holistic, patient-centered care and continuous skill development.
8.1 Educational Requirements
Becoming an IMT practitioner typically requires a degree in a relevant health science field, such as physical therapy, massage therapy, or a related discipline. Specialized IMT training programs focus on manual techniques, holistic approaches, and the integration of multiple therapeutic modalities. These programs are often rigorous and comprehensive, lasting several months to years, depending on the depth of study. The curriculum includes advanced courses in anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics, as well as supervised clinical practice and case studies to ensure proficiency. Continuous professional development is also emphasized to stay updated with evolving techniques and research.
8.2 Practical Training and Hands-On Experience
Practical training is a cornerstone of IMT certification, emphasizing hands-on experience to master manual techniques. Students engage in supervised clinical practice, working with diverse patients to refine diagnostic and treatment skills. Training includes extensive practice in soft tissue manipulation, joint mobilization, and myofascial release. Hands-on workshops and case studies provide real-world application, ensuring proficiency in integrating multiple modalities. Feedback from experienced instructors helps refine techniques, fostering confidence and competence in delivering effective therapy. This experiential learning ensures practitioners are well-prepared to address complex conditions and promote holistic healing.
8.3 Certification Processes and Professional Standards
Certification in IMT involves rigorous training, demonstrating mastery of manual techniques, and adherence to professional standards. Practitioners must complete extensive education and clinical hours, often through accredited programs. Certification ensures competence in IMT’s integrative approach, emphasizing evidence-based methods and ethical practice. Professional standards require ongoing education, ensuring therapists stay updated on advances in manual therapy. Certification validates expertise, fostering trust and excellence in patient care. These standards uphold IMT’s commitment to holistic, effective treatment, ensuring practitioners deliver high-quality, patient-centered therapy.

Integrative Manual Therapy holds exciting possibilities for advancing healthcare, offering a holistic approach to pain management and wellness. Its evolving nature ensures continued innovation and growth.
9.1 The Evolving Field of IMT
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) is continuously advancing, incorporating new research and techniques to enhance its effectiveness. As understanding of the body’s systems deepens, IMT adapts, ensuring it remains a cutting-edge approach in health care. Its evolution is driven by ongoing studies and practitioner feedback, making it a dynamic and responsive therapy. This growth positions IMT as a key player in modern holistic medicine, offering innovative solutions for diverse health challenges.
9.2 Potential for Integration with Other Therapies
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) holds significant potential for integration with other therapeutic modalities, enhancing treatment outcomes. Its holistic approach aligns well with practices like physical therapy, acupuncture, and mind-body therapies. By addressing multiple body systems, IMT can complement psychological therapies, promoting emotional and physical healing. Collaboration between IMT practitioners and other healthcare professionals fosters a comprehensive care plan, tailoring treatments to individual needs. This adaptability makes IMT a valuable addition to multidisciplinary treatment strategies, ensuring a more holistic approach to patient care.
9.3 The Role of IMT in Modern Healthcare
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) plays a vital role in modern healthcare by offering a comprehensive, non-invasive approach to treating pain and dysfunction. Its focus on self-correction and body awareness aligns with current trends toward holistic, patient-centered care. IMT bridges the gap between traditional and alternative therapies, making it an invaluable asset in multidisciplinary settings. By addressing the root causes of pain and promoting overall well-being, IMT supports modern healthcare’s shift toward preventive and integrative medicine, enhancing quality of life for individuals seeking natural, effective treatment options.
